Article originally published on Greencross Vets. Refer to the original article here.
Introduction to puppy teething
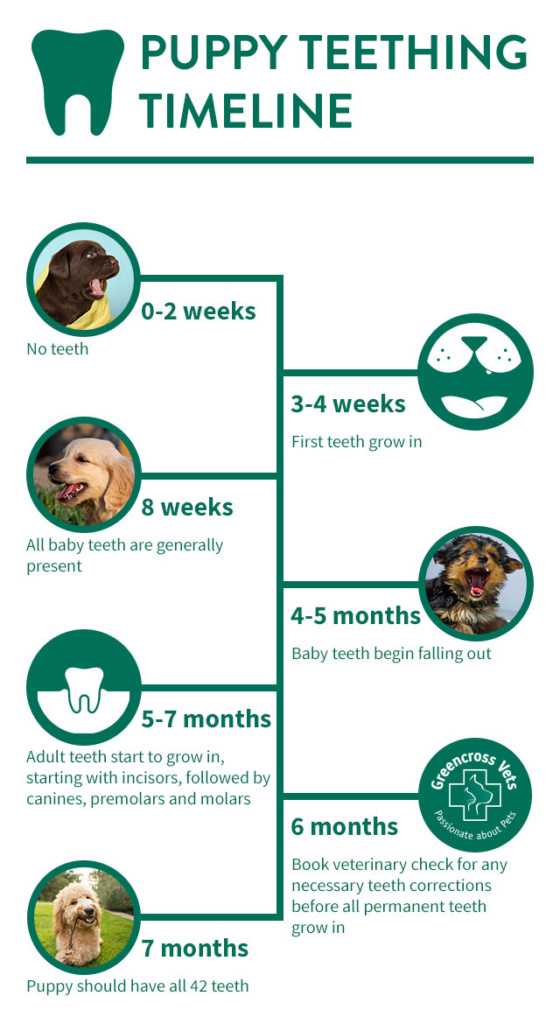
Just like human babies, puppies are born with no teeth. Their first set of baby teeth, or milk teeth, grow in between 3 and 4 weeks of age. When your puppy is around 4-5 months old, these teeth will fall out to make room for their permanent set of adult teeth. By 5-7 months, all the adult teeth will be present. It is important to note this can vary depending on the breed.
This means that puppies experience teething twice, once for their milk teeth and again with their adult teeth. While teething is generally not a painful process for your puppy, they may experience some discomfort in their jaw at this time. The best way to help them alleviate this is to provide your puppy with specifically-designed soft chew toys. This will also prevent unwanted chewing of other objects around the house.
Signs your puppy is teething
- red, inflamed gums
- drooling and offensive breath
- increased chewing behaviour – chewing is the most obvious sign that your puppy is teething and you can help them by providing them with safe toys and discouraging biting
- bleeding gums – a small amount of bleeding from the gums is normal and you may find specks of blood on your puppy’s favourite chew toys
- missing teeth – you may find these on the floor but it is also common and safe for your puppy to swallow these as they fall out
- decreased appetite – puppies may eat slower or less as it causes them discomfort
- puppy in lower mood than usual – some puppies may whine and fuss or be more irritable than usual
When is it necessary to see the vet?
Some puppies experience a slight fever while teething which should be monitored to ensure their temperature does not climb too high.
While teething often involves some bleeding from the gums as your puppy’s sharp teeth emerge, if you notice a large amount of blood, immediately seek professional assistance from your vet.
Before all your puppy’s adult teeth have grown in, you should book them in for a dental appointment at your local Greencross Vets for a precautionary checkup.
What to expect at the dental checkup
The vet will check your puppy for:
- crooked teeth – this can be caused by two teeth coming in at one spot, or if a baby tooth has not fallen out when the adult tooth is emerging. This may be evident during their vaccination checkups
- jaw misalignment – for some breeds with short muzzles, a slight underbite is normal However, if your puppy is showing signs of a strong underbite or overbite, vet intervention may be required to correct chewing and eating issues in the future. These conditions are best treated early
- bad breath – this is not normal in dogs and may indicate that your puppy has a low grade infection
- broken or cracked teeth – if a tooth has broken below the gum line and the nerve is exposed, your puppy will be in discomfort and may develop an infection
- bleeding and swollen gums – this may be a sign of teething
- tartar build up – while tartar build up is uncommon in puppies, it occasionally does happen. Implement a dental routine while your puppy is young to avoid dental diseases in the future
